Transistor As A Switch
суббота 28 марта admin 38
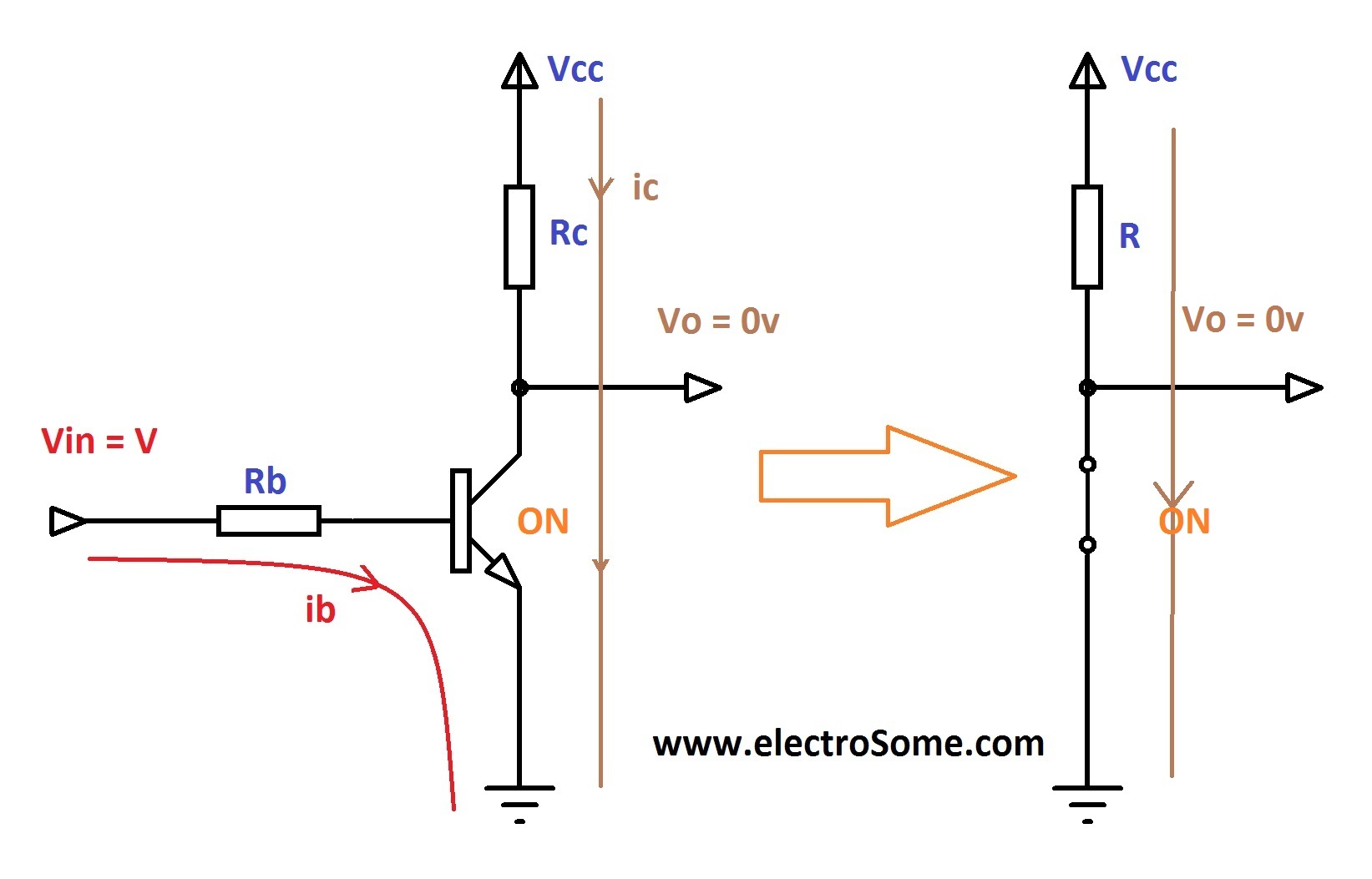
Is a circuit in which the collector of the transistor is switched ON/OFF with relatively larger current in response to a correspondingly switching low current ON/OFF signal at its base emitter.As an example, the following for inverting an input signal for a computer logic circuit.Here you can find that the output voltage Vc is opposite to the potential applied across the base/emitter of the transistor.Also, the base is not connected with any fixed DC source, unlike amplifier based circuits. The collector has a DC source which corresponds to the supply levels of the system, for example 5 V and 0 V in this computer application case.We will talk about how this voltage inversion could be designed to ensure that the operating point correctly switches from cut off to saturation along the load line as shown in the following figure:For the present scenario, in the above figure we have assumed that IC = ICEO = 0 mA, when IB = 0 uA (a great approximation with regards to enhancing construction strategies). Additionally let's assume that VCE = VCE(sat) = 0 V, instead of the usual 0.1 to 0.3 V level.Now, at Vi = 5 V the BJT will switch ON, and the design consideration must ensure that the configuration is highly saturated, by a magnitude of IB which may be more than the value associated with the IB curve seen close to the saturation level.As can be witssed in the above figure, this conditions calls for IB to be greater than 50 uA.
The eldest of the three divine.How to Acquire. She gets up early to prepare something delicious, then gently wakes you up with its tempting smell. Low trigger rate.-Efficiency/ (max):320 / 100(conquest):420/:336/105:441A goddess who oversees breakfast. Games like ayakashi ghost guild.
To use a transistor as a switch, all you have to do is increase the current at the base terminal to a certain level, and the transistor will go into a state commonly known as “saturation.” This is a state (mode of operation) where no matter how much additional current is pumped into the base terminal of the transistor, the collector current. Driving it in either cutoff or saturation mode, the transistor can create the binary on/off effect of a switch. Transistor switches are critical circuit-building blocks; they're used to make logic gates, which go on to create microcontrollers, microprocessors, and other integrated circuits. Below are a few example circuits. Transistor Switch.
Calculating Saturation LevelsThe collector saturation level for the shown circuit can be calculated using the formula. This appears to be perfectly satisfying the required condition.